In the dynamic world of financial markets, traders employ various strategies to capitalize on market opportunities. One such strategy is scalping, a technique that aims to exploit short-term price fluctuations to generate quick profits. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the scalping strategy, its key principles, and considerations for successful implementation.
Scalping is a trading approach that focuses on making numerous rapid trades, aiming to capture small price movements within smaller time frames. This strategy is particularly popular in liquid markets such as commodities, and forex, where price movements occur frequently.
Scalping is a trading strategy known for its fast-paced nature and focus on short-term price movements. Traders who employ scalping techniques aim to profit from small price differentials that occur within a brief timeframe. To effectively execute scalping trades, traders adhere to key principles that guide their decision-making and trading actions:
Scalpers seek highly liquid markets with increased volatility, as these conditions provide greater opportunities for capturing small price differentials. Volatile periods often coincide with economic releases, market openings, or major news events.
Scalpers thrive on shorter timeframes, often utilizing tick charts, one-minute charts, or five-minute charts. These shorter intervals allow them to identify and act upon fleeting price movements more effectively.
Scalpers heavily employ technical analysis tools and indicators to identify short-term trends and potential entry and exit points. Popular tools include moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and stochastic oscillators, among others.

Given the fast-paced nature of scalping, quick execution is vital. Scalpers rely on advanced trading platforms, real-time market data, and high-speed internet connections to facilitate swift order placement and trade management. One favourite tool of scalpers is one-click or one-tap trading, which allows traders to execute trades with just a single click. One-click trading can be enabled on MT4, while one-tap trading can be enabled on the PU Prime App. However, it’s important to note that because one-click/tap trading executes your trade without any additional confirmation, traders should be careful about using it, lest they accidentally put in an unwanted order or trade.
As with any trading strategy, risk management is paramount in scalping. Scalpers utilise tight stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and set predefined profit targets. Adhering to these levels is crucial for disciplined execution.
Scalping strategies using indicators are popular among traders seeking short-term trading opportunities in financial markets. These strategies rely on technical indicators to generate signals for entering and exiting trades. By analysing indicators such as moving averages, oscillators, and volatility bands, traders aim to identify favourable entry and exit points based on specific market conditions. Implementing indicator-based scalping strategies requires a solid understanding of the chosen indicators, market dynamics, and risk management. Here are several commonly utilised scalping strategies that incorporate indicators:
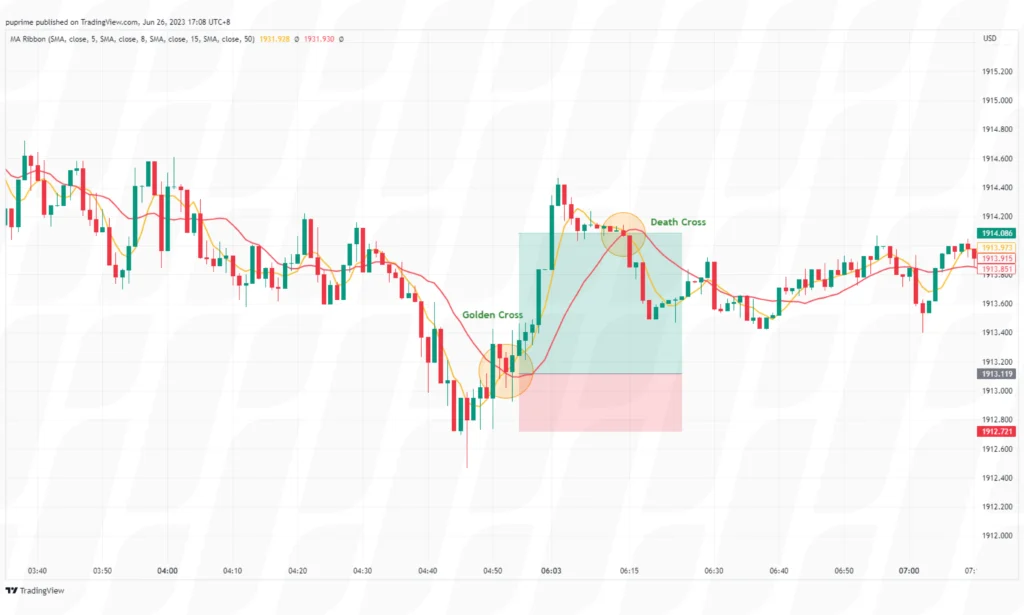
This strategy involves using two moving averages of different periods, such as a fast and a slow moving average. When the fast moving average (e.g., 5-period) crosses above the slow moving average (e.g., 10-period), it may generate a buy signal. Conversely, when the fast moving average crosses below the slow moving average, a sell signal may be triggered.
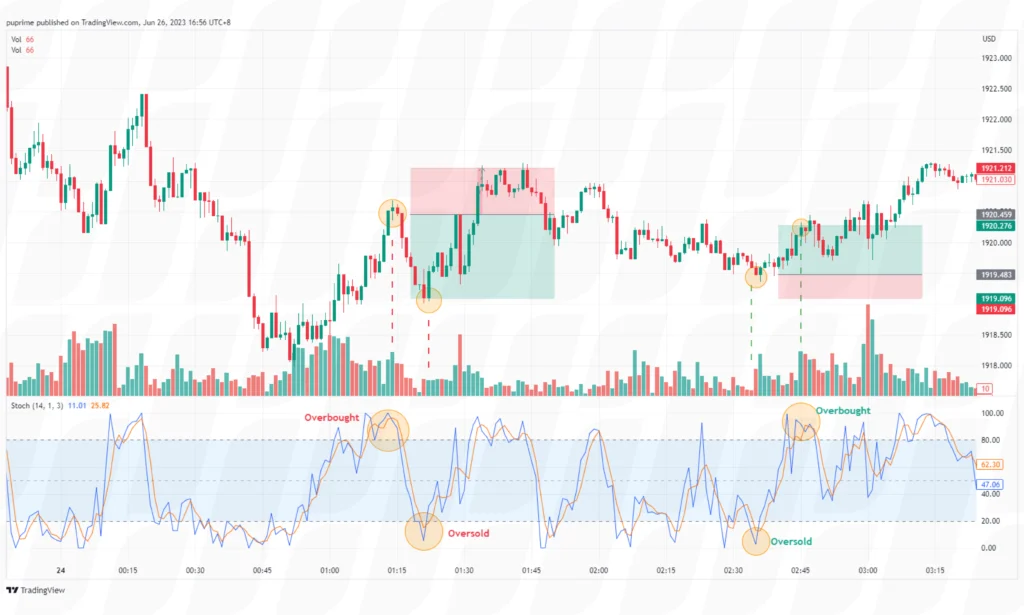
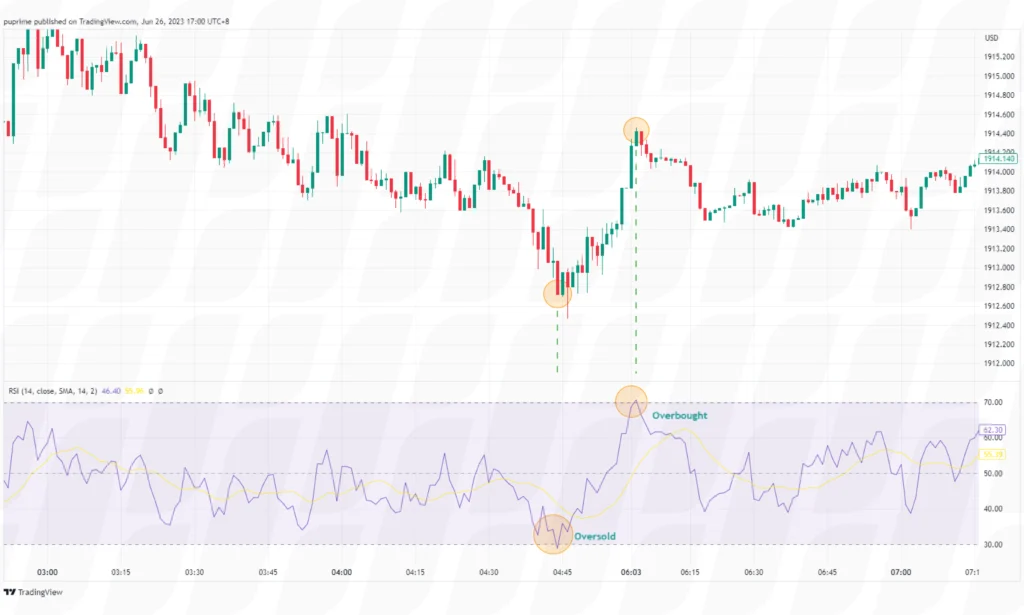
The stochastic oscillator is a popular momentum indicator used in scalping strategies. Traders monitor the oscillator to identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market. When the indicator is in the overbought region (above 80), a potential sell signal is generated, and when it’s in the oversold region (below 20), a potential buy signal is generated.
The RSI is another widely used oscillator in scalping strategies. It measures the speed and change of price movements. Traders look for overbought and oversold conditions in the RSI to identify potential reversal points. When the RSI crosses above 70, it may indicate an overbought condition and a potential sell signal. Conversely, when the RSI crosses below 30, it may suggest an oversold condition and a potential buy signal.
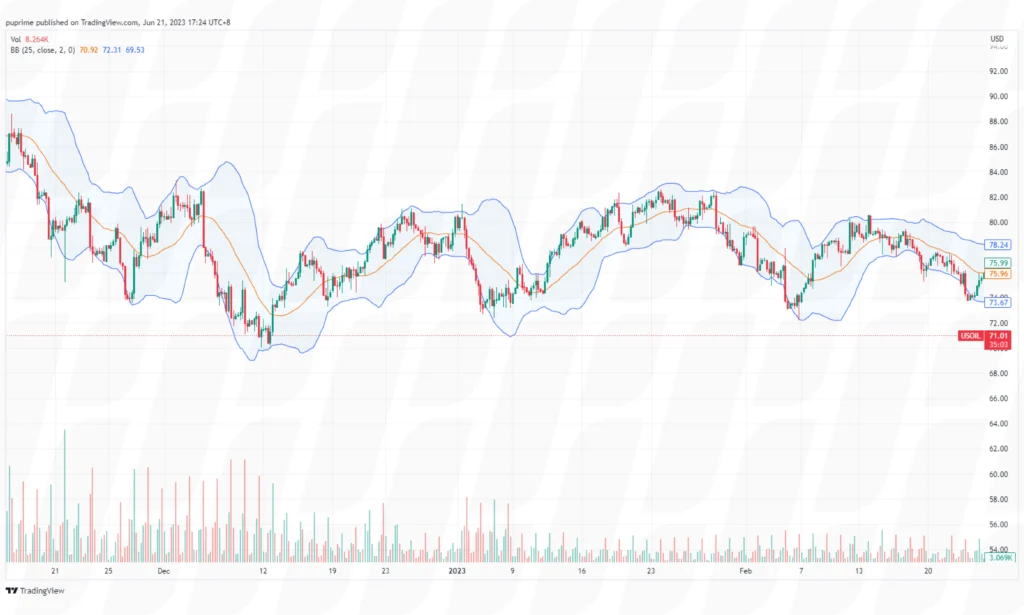
Bollinger Bands consist of a moving average and two standard deviation lines plotted above and below the moving average. Traders use Bollinger Bands to identify periods of low volatility followed by potential breakouts. When the price moves outside the bands, it may indicate a trading opportunity. For example, if the price breaks above the upper band, it could generate a buy signal, and if it breaks below the lower band, it could generate a sell signal.
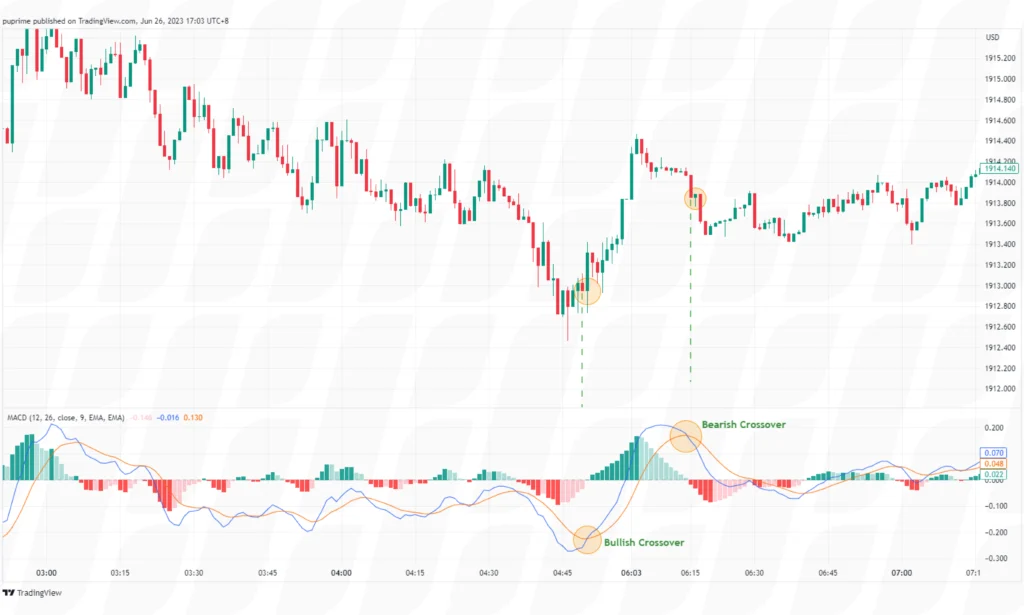
The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator. Traders watch for the MACD line to cross above or below the signal line, which generates buy or sell signals, respectively. Additionally, the MACD histogram, which represents the difference between the MACD line and the signal line, can provide insights into the strength of the trend.
Scalping is a trading strategy that appeals to traders seeking to capitalise on short-term price fluctuations in financial markets. While scalping offers potential benefits, it also comes with its own set of limitations. In this section, we will explore the advantages and limitations of scalping as a trading approach:
While scalping offers the potential for quick profits, it is essential to recognize and understand the risks involved. Traders employing scalping strategies should be aware of the following risks:
Scalping relies on short-term price movements, which can be highly volatile. Sudden market fluctuations or unexpected news events can result in rapid price swings, increasing the risk of adverse price movements and potential losses.
Frequent trading in scalping can lead to higher transaction costs. Commissions, spreads, and slippage can eat into profits, particularly if trading large volumes or using platforms with high transaction fees. Traders must consider these costs and their impact on overall profitability.
Scalping focuses on capturing small price differentials, which limits the profit potential per trade. While these gains can accumulate throughout the trading day, individual trade profits may be modest. Traders must manage their expectations accordingly and aim for consistent gains over time.
Scalping requires constant monitoring of the markets and rapid decision-making. Traders must dedicate significant time and attention, remaining alert to price movements and trade opportunities. The pressure to make quick decisions and manage multiple trades simultaneously can lead to increased stress levels.
The fast-paced nature of scalping can be mentally demanding. Traders must possess discipline, emotional control, and the ability to stick to predefined trading plans. The need for quick decision-making and the potential for consecutive small losses can test a trader’s psychological resilience.
Reliable and fast technology infrastructure is essential for successful scalping. Technical glitches, platform outages, or connectivity problems can disrupt order execution and result in missed opportunities or unintended trade outcomes. Traders should ensure they have a robust trading setup to mitigate such risks.
Scalping is a trading strategy that appeals to individuals seeking short-term opportunities and rapid trade execution. Its focus on capitalizing on small price differentials requires traders to possess a deep understanding of technical analysis, risk management, and market dynamics. While scalping can be rewarding, it also demands meticulous planning, robust technology, and psychological resilience. As with any trading strategy, aspiring scalpers should practice in a risk-controlled environment before deploying their strategies in live markets.

以行业低点差和闪电般的执行速度交易外汇、指数、贵金属等。
